Total angular momentum:
The total angular momentum of an electron is the sum of the orbital angular momentum and spin angular momentum of the electron i.e
Coupling Scheme
Since an atom consist of large number of electrons having different orbital and spin momenta, Coupling scheme is necessary to obtain the resultant orbit and spin momenta of atom as a whole. There are two types of coupling scheme namely
1) LS Coupling
2) JJ Coupling.
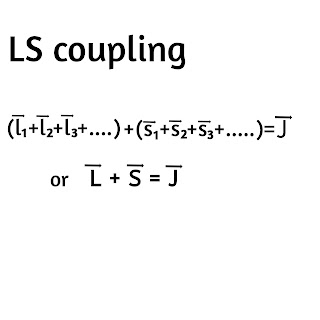
1)LS Coupling:
In this coupling the 'l' vectors of all electrons combine to form resultant 'L' vector and all the 's' vectors of these electrons combine to form resultant 'S' vector. Then the 'L' vector and 'S' vector undergoes vector addition to give resultant 'J' vector which represents the total angular momentum of an atom.
This type of coupling is governed by the following principles:
1) All the three vectors (L,S and J vectors) are quantized.
2)L is an integer including zero i.e L=0,1,2,... etc.
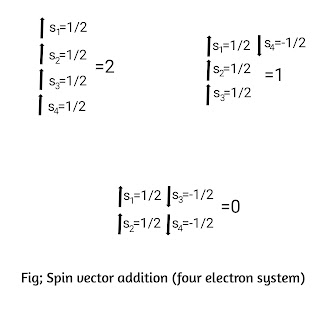
3)S is also an integer or half integer depending upon the number of electrons and the direction of their spin vectors. In case of one electron, the value of S is always 1/2. In case of two electrons S is either 1 or zero depending on whether the spin vectors are parallel or antiparallel. In case of three electron system, S is either 3/2 or 1/2 depending on whether the spin vectors are parallel or antiparallel. In case of four electron system,S=2,1,0 due to the same reason as shown in fig.
Thus S is an integer for even number of electrons and half integer for odd number of electrons.
Since J is the vector sum of L and S, therefore J= integer (0,1,2,3,... etc) when S is an integer or for even number of electrons and J=half integer (1/2,3/2,5/2,7/2,... etc), when S is half integer or for odd number of electrons.
4)J is always positive and never negative.
This type of coupling is commonly used.
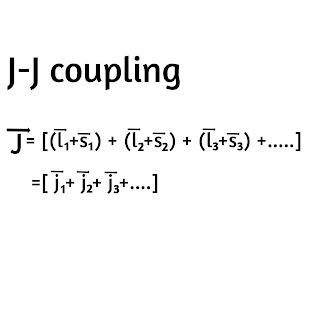
2) J-J Coupling
In this coupling, each electron is considered seperately and its contribution to the total angular momentum of the atom is obtained by combining first the individual spin and orbital angular momentum vectors using the relation
Then the total angular momentum vector of the atom will be the vector sum of the individual j vector of the electrons. This type of coupling may be represented as
This type of coupling is rarely used.

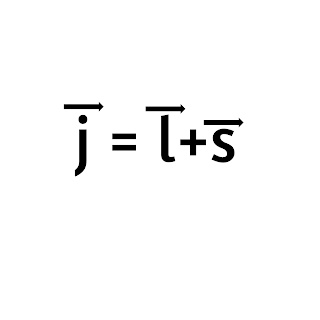
Comments
Post a Comment